PD Fast charge protocol in USB charger
I. Introduction
USB-Power Delivery (USB-PD) is one of the mainstream fast charge protocols. It is a fast charging specification developed by the USB-IF organization. USB-PD increases power delivery through USB cables and connectors, extending cable bus power capabilities in USB applications. The specification enables higher voltages and currents, delivers power up to 100W, and can freely change the direction of power delivery.
Relationship between USB-PD and Type-C. There are often people who put USB-PD and Type-C together, and even call the Type-C charger PD charger. USB-PD and Type-C are actually two different things, USB-PD is a fast charging protocol, and Type-C is a new interface specification. The Type-C interface supports a maximum of 5V/3A by default, but after the implementation of the USB-PD protocol, the output power can be supported up to 100W. So now many practical Type-C interface devices will support the USB-PD protocol.
The development prospect of USB-PD. USB-PD has now evolved to USB-PD3.0. Under the promotion of Google, USB-PD has incorporated Qualcomm’s QC fast charge agreement and obtained the support of China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology. It is expected to unify the current chaotic fast charging source market in the near future.
II. Can PD charging protocol and QC charging protocol be mixed
Although the Android camp has its own fast charge technology, QC3.0 is compatible with them. Since the vast majority of Android phones on the market use Qualcomm chips or baseband, naturally Qualcomm QC3.0 can fast charge Android phones.
We all know that more than iPhone8 models support fast charging, so QC3.0 charger can give iPhone8 fast charging? It can charge, but it can’t turn on fast charge for the iPhone. The PD charger is an all-purpose fast charge, it can not only give more than iPhone8 models for fast charge (with C94 terminal head MFi certified C to Lighting fast charge line), but also compatible with QC3.0 charging protocol to the market mainstream Android mobile phones for fast charge. In this way, it is more cost-effective to buy a PD charger, that is, you can fast charge Android phones, and you can also fast charge iphones.
III. Do PD fast charge and QC fast charge share the same data cable
In fact, PD fast charge and QC fast charge protocols although there are some differences, but they all use the USB Type-C interface, both support fast charging function.
At present, the PD protocol supports the QC protocol, and it is worth noting that the PD data cable is a USB-C TO USB-C interface, and the QC data cable is a USB-A TO USB-C interface. Therefore, PD fast charge and QC fast charge can be charged using the same data line. The premise is that the data cable meets the USB specification and can support fast charging function.
However, due to the large power of PD fast charge, it is recommended to choose a data cable that can support PD fast charge when using PD fast charge to achieve the best fast charge effect. If the QC fast charge protocol is used for charging, it is best to choose a data cable that can support QC fast charge.
In short, in order to ensure the charging safety and charging effect, it is recommended that users carefully check the product specifications when selecting the data cable, and choose the appropriate data cable according to their own needs.
The USB power adapter produced by JPT Power complies with the PD fast charge protocol, so
IV. PD protocol in the battery charging application
1. First consider the acceptance capacity of the battery.
Charging is like feeding the battery, so you need to know how the battery feels. At present, the battery capacity of smart electronic devices on the market is basically 3700~4600mAH. Assuming a maximum voltage of 4.35V and 1.5C charging, the maximum possible charging power is 20W, but this is only the limit case. In addition to the power reception capability, the current reception capability also needs to be considered. For a 3000mA battery, at 1.5C charging, the charging current will reach 4.5A, so the battery contacts and the current transmission structure inside the cell need to be optimized.
2. The second need to consider the power supply capacity of the adapter.
Without considering the capacity of the interface, providing 20W power is a breeze for the adapter. However, the traditional Micro USB interface in the standard specification of the maximum current carrying capacity is 2A, the highest voltage is 5.25V, can only provide 10.5W power, can not meet the requirements of 20W. So how do you solve this problem?
There are obviously two solutions, one is to increase the current, the other is to increase the voltage. However, if the physical interface is not changed, increasing the current is not possible, so increasing the voltage is the only option in the Micro USB era, which is the origin of Qualcomm QC fast charging method. Therefore, it can be seen that the QC standard recommends a current of 1.5A, because 2A is the limit of Micro USB. The general consensus in the industry is not to use the device to the limit value, but to reserve the margin.
In this respect, OXXO has taken the opposite path from Qualcomm. They have physically patched Micro USB, adding extra contact pins specifically designed to transmit high currents. The maximum charging current reached 4.5A, but the voltage remained unchanged at 5V, also achieving a power transfer of more than 20W. The emergence of the Type-C interface makes this problem no longer exist, because the TYPE-C port supports up to 5A input current, which can fully meet the fast charging needs of existing mobile phone batteries.
3. In addition, the charging management and heat dissipation capacity of the mobile phone also need to be considered.
Charge management must involve voltage conversion, constant current control and other links, which will inevitably bring about the reduction of charging efficiency and heat dissipation problems. Therefore, in theory, the best charging design scheme is that the internal charge management of the mobile phone is not done, and the external adapter is completely controlled. At this point, QC is at a loss, because high power and low current input will inevitably lead to energy conversion inside the mobile phone, into low voltage and high current, which will bring about problems in the heat dissipation of the mobile phone. Therefore, from a technical point of view, the historical limitations of QC have been highlighted. The more serious problem is that the TYPE-C interface and USB-PD are strictly prohibited from using ways other than USB-PD to adjust the charging voltage. Although Qualcomm has made great efforts to try to allow QC and PD to exist simultaneously in the TYPE-C interface, it is a pity that it was ruthlessly rejected, and the latest TYPE-C1.2 and USB-PD3.0 maintain the description of this feature. Therefore, QC will face the danger of being eliminated both technically and theoretically. Of course, Qualcomm itself is already aware of this trend. Therefore, in the latest processor core, the negotiation function of USB-PD is integrated.
V. USB-PD fast charging communication principle
As shown in the figure, in USB-PD communication, 24MHz FSK is coupled to the DC level of VBUS through cAC-Coupling coupling capacitors. In order to ensure that 24MHz FSK does not affect the VBUS DC voltage of Power Supply or USB Host, A low-pass filter composed of zIsolation inductors is also added to the loop to filter out FSK signals.
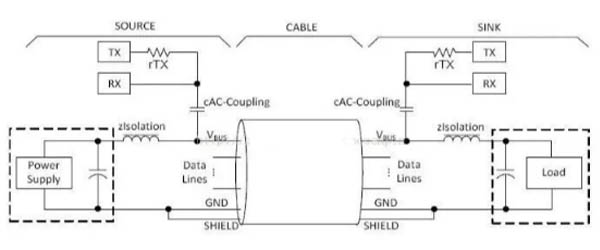
The principle of USB PD, with mobile phones and chargers supporting USB PD as an example, is explained as follows:
1) USB-OTG PHY monitors VBUS voltage, if there is a VBUS 5V voltage exists and the OTG ID pin is detected to be 1K pull-down resistance (not OTG Host mode, OTG Host mode ID resistance is less than 1K), it means that the cable supports USB PD;
2) USB-OTG performs normal BCS V1.2 charger detection and starts the USB PD device policy manager, which monitors whether the VBUS is coupled with FSK signals on the DC level and decodes the Capabilities Source message. Analyze the message according to USB PD specification to get all the voltage and current list pairs supported by USB PD charger;
3) The phone selects a voltage and current pair from the Capabilities Source message based on the user’s configuration, and adds the voltage and current pair to the payload of the Request message, and then the policy manager couples the FSK signal to the VBUS DC level;
4) The charger decodes the FSK signal and sends an Accept message to the phone, while adjusting the DC voltage and current output of the Power Supply;
5) After receiving the Accept message, adjust the charging voltage and current of the Charger IC;
6) During the charging process, the mobile phone can dynamically send a Request message to request the charger to change the output voltage and current, so as to achieve the process of fast charging.
VI. Conclusion
In summary, USB-Power Delivery (USB-PD), as a fast charging protocol, has developed rapidly in recent years. Compared with other fast charge protocols, USB-PD can achieve higher voltage and current, deliver power up to 100W, and is not limited to one-way power delivery.
At the same time, in terms of charging equipment, PD charger is an all-purpose fast charge, which can be used for fast charging of more than iPhone8 models, and can also be compatible with QC3.0 charging protocol for fast charging of mainstream Android phones on the market. In addition, PD fast charge and QC fast charge protocols can also share the same data cable for charging, provided that the data cable conforms to the USB specification and can support fast charging functions.
In terms of battery charging, the PD protocol needs to consider the acceptance capacity of the battery, the power supply capacity of the adapter, and the charging management and heat dissipation capacity of the phone. Finally, we would like to remind users that when choosing a data cable or charging device, they need to carefully review the product specifications and choose the appropriate power adapter products according to their needs.
JPT Power is a professional power adapter supplier in China. Our products are compatible with a variety of charging protocols to provide a safer, faster and more efficient charging experience for your mobile phones and electronic devices.






